

This might show you a list of access points and connected devices. Next, we want to get an overview on wireless networks in our area: airodump-ng wlan0 You can check the right value using iwconfig. Note: Instead of wlan0 you might need to user another interface. Hence, you can basically immediately start with putting your NIC into monitor mode: airmon-ng start wlan0 However, in my tests I usually did not have problems even if I did not run that command. Aircrack-ng suggests to run the following command: airmon-ng check kill Next, when you have booted up your Kali Linux, you might want to kill processes which could interfere with your tests. I explained this before with a specific example. What you will also realize is that using WPA2 together with a strong password is an effective protection against such attacks.įirst, make sure that your WiFi adapter is working properly with Kali. You will see, it’s really easy, but I will also give some tips on what to do if things go awry. Therefore, I thought to write down the few steps which you actually need. While I was looking up some things for the aircrack-ng suite, I realized that most tutorials on how to get started with cracking wireless encryption seem to be quite complicated – or they lack essential information.Īctually, there’s really not a lot you need to do to get started. Please let me know if more information is needed.In the previous post I explained how to set up your Alfa WiFi adapter to perform security tests on your wireless network. But knowing that it might just be me not fully understanding how everything works, I was hoping to get some insight from this community.įor what it's worth, I'm using Airbase-ng 1.2 rc4 and running cat /etc/issue shows Kali GNU/Linux Rolling \n \l. From what I have found online, the network adapter I am using is not one of the most popular ones, so I'm willing to buy a new one if that's the reason.
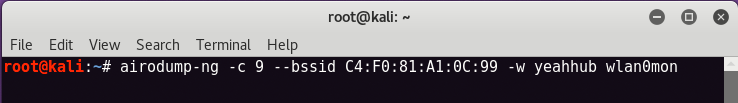

My question, then, is whether this is normal or not. Sometimes the second approach will work and other times it won't. When I try to use any of these various methods, I get varied results.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
